OEE availability of machines and operators
The analysis of unproductive stoppages allows us to go deeper into the causes that lead to low availability, and to apply continuous improvement actions until high availability is achieved.
doeet analyzes the actual OEE availability of all production lines, their deviation from their target, the machine hours in operation, downtime or non-operational time, the causes of line stoppages, as well as their duration, frequency and their evolution over time.
The doeet system collects in real time the operating statuses of the machines(running, stopped, non-operating time) by means of the
MES system
The doeet system collects in real time the operating statuses of the machines (running, stopped, non-operating time) by means of the plant data acquisition system and calculates the percentages of the machines in each status.
doeet also collects the justifications for stoppages made by operators at the machine via HMI terminals. We can customize the causes of stoppage and group them into categories, so that it is quick and easy for the operator to indicate them at the machine.

- Know the actual uptime of your machines and how much they have deviated from their target.
- Know in real time the machine hours in operation, machine downtime and non-operational times.
- Knows the causes of stoppages, their frequency and their evolution when applying improvement actions in production.
From real availability to high availability OEE
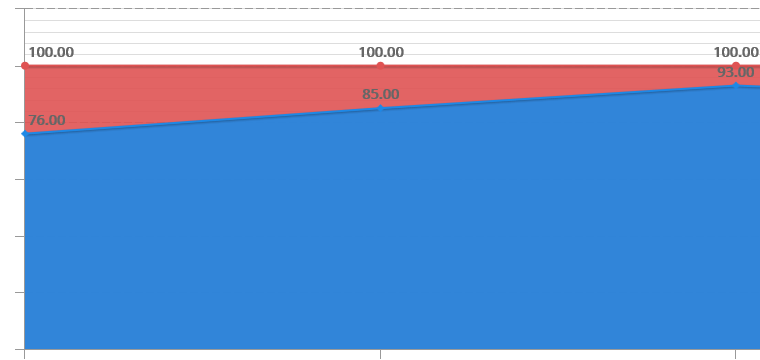
doeet indicates the actual availability of all production lines and compares these values with our OEE high availability targets to analyze their deviation and the causes for it.
The OEE availability targets per line, per shift or per reference are taken as a reference to measure the availability deviation and to make informative and visual indications.
doeet also shows the detail of machine hours in actual run (HMMR), theoretical run (HMMT), actual stop (HMPR) and theoretical stop (HMPT), as well as the total units produced.
Analyze your shutdowns by line, shift, order, reference
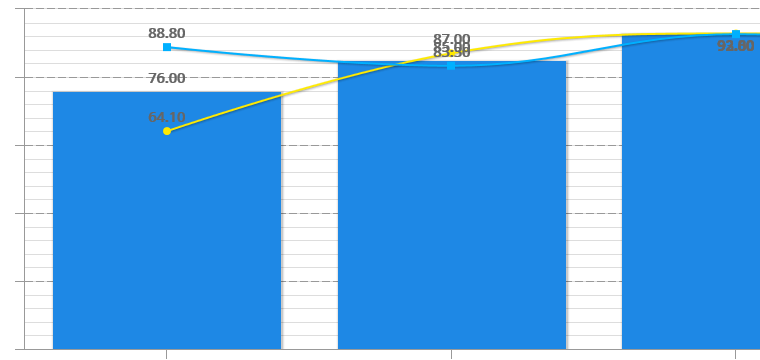
doeet allows you to filter the production information by line, reference, production order or shift, in order to drill down to the causes of low availability.
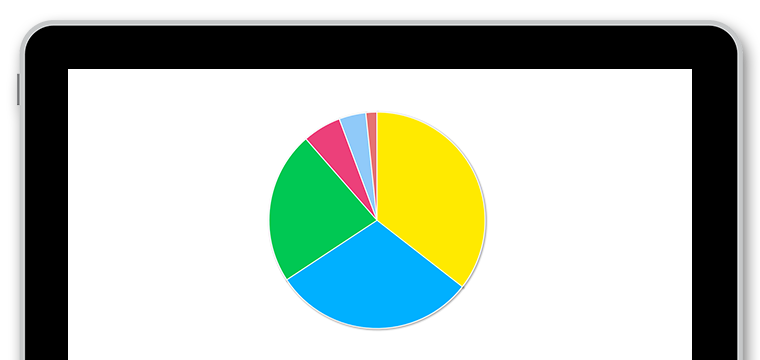
The availability per line indicates the actual OEE availability collected from each of the production lines and its chronological evolution, as well as the high availability targets for each line.
doeet also shows in detail the actual machine running hours (HMMR), actual downtime (HMPR) and HM(PTB), as well as the total units produced on each of the lines.
Know your causes of shutdowns…
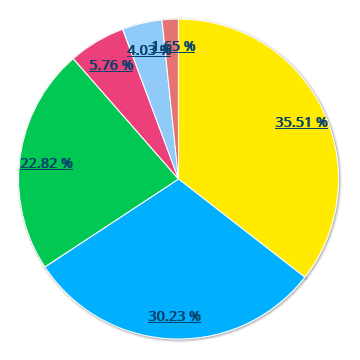
Production stoppages are usually grouped for analysis and improvement into different groups of stoppages, usually organizational causes, breakdowns, cleaning, changes, etc.
doeet allows us to customize the most common causes of stoppages in our production and group them into categories, so that it is easy and quick for the operator to justify the stoppages at the machine using the doeet terminal.
… and reduces the most frequent
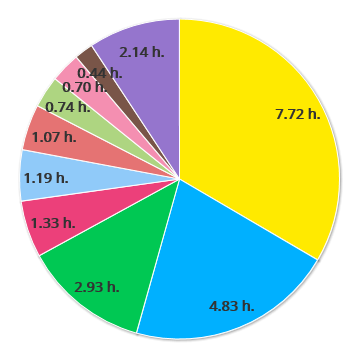
Analyzing the most frequent causes of downtime and taking measures to avoid them will increase the OEE availability of our machines and operators and improve your productivity.
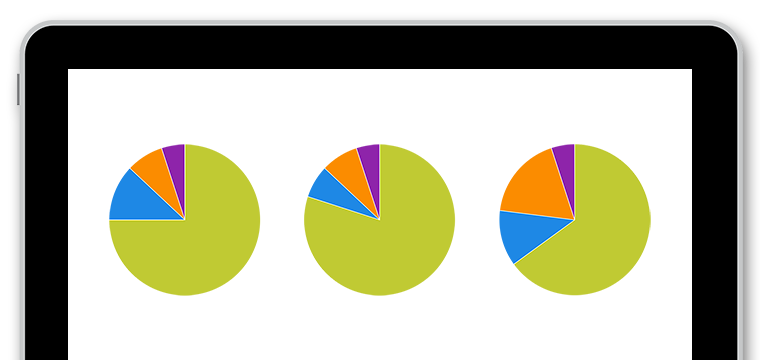
doeet represents the 10 causes of downtime that imply the greatest loss of OEE availability and productivity in hours and percentage.
Hours and frequency of stoppages and micro-stoppages
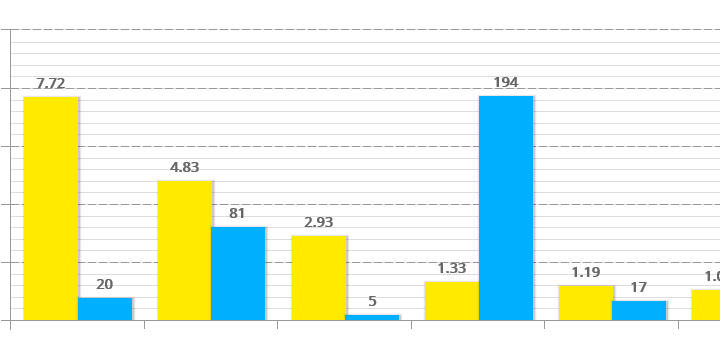
There are stoppages that occur infrequently during production but consume a large amount of time, such as breakdowns, and others, such as micro stoppages, that occur very frequently but involve only a few hours of production downtime.
Simultaneously visualizing the hours and frequency of each of the most frequent stoppages helps us to understand how each cause of stoppage affects our production.
High availability OEE for Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 marks important challenges in product manufacturing, such as optimizing operations and using more flexible, smarter and more available systems.
An unscheduled shutdown due to system failure can have very serious implications for production and very high costs. The process industry worldwide loses 5% of its annual production due to unscheduled downtime.
High availability OEE arises in response to this need, ensuring that machines, operators and systems are available at all times and without interruption.
High availability is not necessary for all types of systems. In industrial environments, there are critical systems and other systems that are not so critical. A well-known way of expressing availability is by means of “nines”. Three nines of availability (99.9%) may seem like a good target, but depending on the criticality of the process, it can be catastrophic.
The basis of Industry 4.0 is the availability of all relevant information in real time, and this is achieved by connecting all elements of the value chain.
Price Waterhouse Cooper: “Opportunities and challenges of the industrial internet”.
Reliability, maintainability, availability
In real-time productivity monitoring systems, downtime is a fundamental part of business planning systems. The solutions to improve our plant production indicators include the analysis of the OEE and its component factors: availability, performance and The points to be taken into account when choosing a quality The OEE high availability system is based on three indicators that will help us to analyze our plant systems: Reliability, maintainability and availability.
Reliability
Reliability is the probability that a device will perform the function for which it is designed under specified conditions and over a specified period of time, and is quantified by a system’s mean time between failures (MTBF).
Eliminating the main causes of machine failure significantly increases MTBF. For this reason, the first thing to do is to identify the most faulty elements and try to eliminate or mitigate their faults. This ensures that the overall MTBF of our system increases and therefore reliability.
Reliability =
Total manufacturing time
Total number of failures
Maintainability
Maintainability measures how long it takes a machine to return to a normal operating state after a system failure, and is measured by mean time to repair (MTTR). This value is more difficult to calculate, since it depends on the replacement time and the complexity of the machine or the failure produced.
The average repair time can vary from minutes to weeks.
Mean time to repair (MTTR) is difficult to calculate and can vary from minutes to weeks.
Availability
Availability is a function of reliability and maintainability, and defines the percentage of time the system is operational.
Maximizing availability requires increasing MTBF and decreasing MTTR.
The availability can be calculated with the equation: